Tube Calculator
Calculate the various properties of a tube (hollow cylinder) given 3 known values from variables of radii, circumference, wall thickness and height.
| Property | Value | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Radius (r₁) | – | C₁/2π or √(V₁/πh) or √(L₁/2πh) or r₂ + t |
| Inner Radius (r₂) | – | C₂/2π or √(V₂/πh) or √(L₂/2πh) or r₁ – t |
| Height (h) | – | L₁/2πr₁ or L₂/2πr₂ or V₁/πr₁² or V₂/πr₂² or V/A |
| Wall Thickness (t) | – | r₁ – r₂ |
| Outer Circumference (C₁) | – | 2πr₁ |
| Inner Circumference (C₂) | – | 2πr₂ |
| Outer Surface Area (L₁) | – | 2πr₁h |
| Inner Surface Area (L₂) | – | 2πr₂h |
| Volume within Outer (V₁) | – | πr₁²h |
| Volume within Inner (V₂) | – | πr₂²h |
| Volume of Solid (V) | – | π(r₁² – r₂²)h |
| End Surface Area (A) | – | π(r₁² – r₂²) |
Cite this content, page or calculator as:
Appreciate our scientific content creators and cite this page. Your support matters and keeps us motivated!
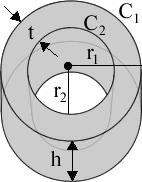
r1 = outer radius
C1 = outer circumference
L1 = outer surface area
V1 = volume within C1
r2 = inner radius
C2 = inner circumference
L2 = inner surface area
V2 = volume within C2
h = height
t = wall thickness
V = volume of solid
A = end surface area
π = pi = 3.1415926535898
√ = square root
Tube Calculator
Tube Calculator is a quick and accurate tool that helps you find the volume, surface area, and wall thickness of a tube — also known as a pipe or a hollow cylinder. By entering just three known values such as radii, height, or wall thickness, the calculator automatically determines all related measurements of the tube.
Whether you’re working on a plumbing project, mechanical design, or classroom geometry problem, this calculator delivers instant results in any unit — from millimetres to feet — without the need for manual conversions.
What Is a Tube?
A tube (or hollow cylinder) is a 3D geometric shape with a circular cross-section and a hollow center. It has two main circular surfaces — outer and inner — separated by a wall thickness.
If you slice a tube horizontally, the end view looks like an annulus — a ring-shaped region between two concentric circles.
Tube Calculator Formula Overview
All tube calculations are based on standard geometric formulas derived from the cylinder.
If you know any three of these — outer radius (r₁), inner radius (r₂), height (h), or wall thickness (t) — you can find the rest easily.
1. Tube Circumference
Outer circumference:
C₁ = 2πr₁
Inner circumference:
C₂ = 2πr₂
These give you the perimeters of the outer and inner circles of the tube.
2. Lateral Surface Area
The lateral (side) surface area represents the curved surface of the tube.
Outer lateral area:
L₁ = 2πr₁h
Inner lateral area:
L₂ = 2πr₂h
3. Cross-Sectional Area
The cross-sectional area (the ring shape at each end of the tube) is calculated as:
A = π(r₁² − r₂²)
This value also represents the solid area of the tube’s end profile.
4. Tube Volume
The total volume enclosed by the tube is the product of its cross-sectional area and height:
V = π(r₁² − r₂²)h
This gives you the tube’s material volume — excluding the hollow space inside.
5. Tube Wall Thickness
Wall thickness is simply the difference between the outer and inner radii:
t = r₁ − r₂
If you know the outer and inner diameters instead of radii, divide each by 2 before applying the formula.
Units and Dimensional Consistency
All formulas above work in any unit system.
- If r and h are in millimetres, the resulting volume will be in mm³.
- If you use inches or feet, your result will be in cubic inches or cubic feet respectively.
Changing the input units will only scale the result — not change the relationships between values.
How to Use the Tube Calculator
Using the Tube Calculator on CalculatorCave is straightforward:
- Enter any three known values – such as outer radius, inner radius, and height.
- The calculator automatically solves for the remaining values (volume, wall thickness, surface area, etc.).
- Select or note your preferred units (mm, cm, m, or ft).
- Click Calculate to view instant, precise results.
This step-by-step process eliminates the need for manual math and avoids conversion mistakes.
Practical Example: Tube Volume Calculation
Let’s assume you have a steel pipe with the following measurements:
Outer radius (r₁) = 5 cm
Inner radius (r₂) = 4 cm
Height (h) = 10 cm
Now plug the values into the formula:
V = π(r₁² − r₂²)h
V = 3.1416 × (25 − 16) × 10
V = 3.1416 × 9 × 10 = 282.74 cm³
So, the tube’s volume is approximately 282.74 cubic centimetres.
Understanding Tube Geometry
A tube behaves like a cylinder with its inner portion removed.
To visualize this better, explore related shapes:
- A solid cylinder has only one radius and is fully filled with material. See Cylinder Calculator for comparisons.
- A conical frustum shows similar volume subtraction logic but for cones. You can explore it with the Conical Frustum Calculator.
- A sphere or hemisphere also shares circular cross-sections and similar surface relationships. Check the Hemisphere Calculator to see how circular area formulas extend to 3D curvature.
Each of these shapes relies on the same geometric foundation — πr² relationships — making the tube a simple yet essential case in applied geometry.
Why Use a Tube Calculator?
Manual calculations can become error-prone, especially with small measurements or multiple unit conversions.
The Tube Calculator offers:
- Instant computation of volume, surface area, and thickness.
- Flexible inputs (any three known values).
- Support for all common units.
- Consistency with engineering, manufacturing, and academic standards.
This makes it a practical utility for engineers, builders, designers, students, and anyone working with pipes or hollow materials.
Common Questions (People Also Ask)
1. What is the formula for tube volume?
Tube volume formula: V = π(r₁² − r₂²)h
2. How do I find the wall thickness of a pipe?
Wall thickness t = r₁ − r₂, where r₁ is the outer radius and r₂ is the inner radius.
3. How do I calculate the cross-sectional area of a tube?
A = π(r₁² − r₂²). This gives the material area of the tube’s end face.
4. Can I calculate tube volume in different units?
Yes. Use consistent input units (e.g., mm, cm, m). The output will automatically scale — for instance, using mm gives mm³ for volume.
5. What’s the difference between a tube and a cylinder?
A cylinder is solid, while a tube is hollow. The Tube Calculator accounts for the hollow space, subtracting the inner volume from the outer volume.
Tube Calculator Applications
The Tube Calculator is widely used in:
- Plumbing – to estimate pipe material volume.
- Manufacturing – for metal and plastic tube fabrication.
- Construction – to plan concrete or pipe dimensions.
- Academic projects – to teach geometry and measurement concepts.
Because it works from basic geometric relations, it applies to any tube, regardless of scale or material.
Tube Calculation Summary
| Property | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Circumference | C₁ = 2πr₁ | Perimeter of the outer circle |
| Inner Circumference | C₂ = 2πr₂ | Perimeter of the inner circle |
| Lateral Surface Area | L₁ = 2πr₁h, L₂ = 2πr₂h | Curved outer and inner surfaces |
| Cross-Sectional Area | A = π(r₁² − r₂²) | Ring-shaped end area |
| Volume | V = π(r₁² − r₂²)h | Material volume |
| Wall Thickness | t = r₁ − r₂ | Tube wall thickness |
Tube vs. Pipe — Are They the Same?
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, there’s a small difference:
- Tube usually refers to structural or geometric analysis (focus on shape and material).
- Pipe often refers to flow systems (focus on internal diameter for fluids).
However, for most geometric and engineering calculations, both follow the same formulas — which the Tube Calculator supports.
Advantages of CalculatorCave’s Tube Calculator
- User-friendly layout optimized for both desktop and mobile.
- Instant computation engine — no waiting or loading delays.
- Accurate geometric formulas verified for dimensional correctness.
- Multi-calculator integration with related geometry tools for quick reference.
- LLM-readable structure, increasing your content’s visibility in AI-generated summaries and responses.
Explore More Geometry Tools
If you’re learning or calculating geometric shapes, expand your understanding with these tools:
- Volume Calculator – to find the volume of different 3D solids.
- Surface Area Calculator – to compute total exposed area for any solid.
- Geometric Shapes Tool – to explore relationships among 2D and 3D forms.
Each of these complements the Tube Calculator for a complete geometric workflow.
The Tube Calculator simplifies every step of tube-related measurement — from finding wall thickness and circumference to calculating volume and surface area. It’s precise, fast, and compatible with any unit, making it essential for engineers, students, and makers alike.
Use it to turn geometry into instant, reliable results — whether you’re building, designing, or simply exploring the elegant math behind everyday structures.
